|
|
 |
Back to Annual Meeting Posters
Predictors of Obtaining a Non-Diagnostic Renal Duplex Ultrasound
Samantha Minc, MD, Ian Daniel, MD, Ruta Ausraite, Theodore Karrison, PhD, Laurie Lozanski, RVT, Mohammad Elsorady, MD, Christopher Skelly, MD, Darwin Eton, MD, Ross Milner, MD, Robert C. Steppacher, Jr., MD.
University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA.
OBJECTIVES:
Renal duplex ultrasound (RDUS) is technically demanding, and is often incomplete or non-diagnostic. The purpose of this study is to determine the incidence of non-diagnostic renal duplex ultrasound (NDRDUS) at our institution and to determine if a NDRDUS may be predicted by examining factors available in the electronic medical record at the time the study is ordered.
METHODS:
A retrospective chart review was performed for all adult patients who underwent RDUS of the native renal arteries at our institution from 10/1/2010 to 10/1/2011. Age, vital signs, body mass index (BMI), medical comorbidities, diagnosis, fasting time, study time, study location, equipment type, and technician experience were examined. The primary end point was achieving a non-diagnostic study. Univariate and multivariate regression analysis were employed to evaluate the influence of physiological and demographic factors on the outcome of the RDUS.
RESULTS:
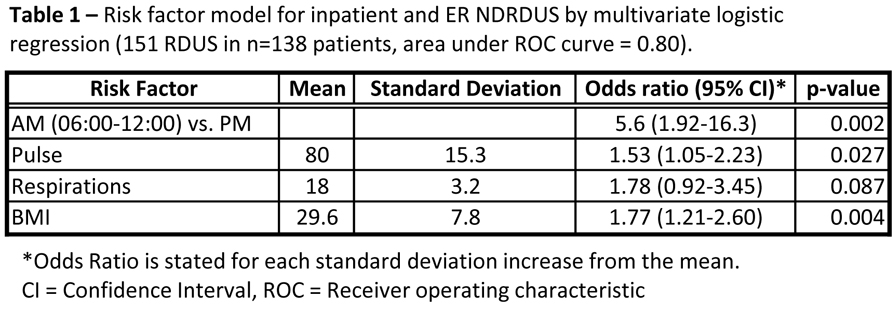
During the study period a total of 253 ultrasounds were performed in 236 patients. Ninety nine studies were performed on outpatients, 144 on inpatients, and 10 on emergency room (ER) patients. 18/99 (18%) outpatient studies were non-diagnostic, 92/144 (64%) inpatients studies were non-diagnostic and 5/10 (50%) ER studies were non-diagnostic. Analysis of the outpatient cohort failed to identify any variables, including BMI, predictive of NDRDUS. On multivariate analysis of the inpatient and ER cohort time of day, pulse, respiratory rate, and body mass index (BMI) were found to be predictive of NDRDUS (Table 1).
CONCLUSIONS:
The incidence of NDRDUS is greatly increased in inpatients vs. outpatients. For hospital inpatients the likelihood of obtaining a non-diagnostic RDUS is influenced by the time of day, heart rate, respiratory rate and BMI. Diagnostic yield can be increased by performing RDUS in the morning, and taking into account the patient’s BMI, pulse and respirations.
Back to Annual Meeting Posters

|


