Back to Karmody Posters
Community - Based Walking Exercise Intervention in Hispanic patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) - Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
David E. Timaran, M.D., Eric B. Rosero, M.D., Adriana Higuera, M.D., Daniel Walk, M.D., Luis F. Gomez, M.D., Mirza S. Baig, MD, Carlos H. Timaran, M.D..
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.
OBJECTIVE: To determine whether a community-based walking exercise program that uses a group-mediated risk modification intervention, can improve functional performance compared to usual care and unsupervised control group in patients with PAD with and without intermittent claudication.
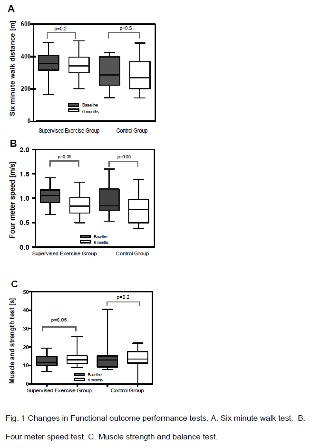
METHODS: Randomized controlled clinical trial of 53 Hispanic patients with PAD was performed in Dallas, Texas during a 12-month period. Participants were randomized to 1 of 2 parallel groups: community-based walking exercise intervention or usual care unsupervised control group. The primary outcome was 6-month change in 6-minute walk performance. Secondary outcomes included 6-month change in 4-meter walking velocity and muscle power balance.
RESULTS: Participants randomized to both groups had a decline in their performance in the 6 minute walk test (reported in meters): intervention group, 357.3 (IQR 316.2-405.7) to 342 (IQR 301.8-396.3); control group, 286.5 m (IQR 224-397.8) to 268.5 (IQR 202-368). Median difference was -16.4 meters for the intervention group (P=0.2) and -15.05 meters for the control group (P=0.5). In the 4-meter walking velocity test, patients from both groups had a decrease in the walking speed: intervention group, 1.06 to 0.84 m/s (p=0.05); control group, 0.85 to 0.77 m/s (p=0.05). Patients in both groups required more time to complete the muscle balance test (intervention, 11.6 to 13.15 seconds [p=0.06]; control, 12.95 to 13.55 seconds [p=0.2]).
CONCLUSION: A community- based walking exercise program did not improve walking distance, endurance and walking speed in Hispanic patients with PAD with and without claudication symptoms. Future studies are required to evaluate the effectiveness of alternative non-Hospital based exercise programs in patients with PAD, especially for patients from ethnic minorities.
Back to Karmody Posters

|


