Back to 2016 Karmody Posters
Patient Characteristics Associated with Active Smoking Upon Presentation with Claudication Symptoms to Specialty Clinics: Insights from the PORTRAIT Registry
Mark Friedell, MD, Kim Smolderen, PhD, John Spertus, MD, Scott Hardouin, MD, Kim Dyer, RN, Robert Corn, MD, Kensey Gosch, MS, Nancy Stone.
University of Missouri Kansas City, Kansas City, MO, USA.
Objective: In patients with claudication, smoking is an important factor in treatment selection, since it is a potent risk factor for graft or endovascular treatment failure. Given these selection biases, observational, comparative effectiveness studies of claudication treatment need to adjust for other potential patient characteristics associated with smoking. Comparing the clinical and psychological characteristics of patients with claudication who do and do not smoke has not been described and is essential for future research in the field.
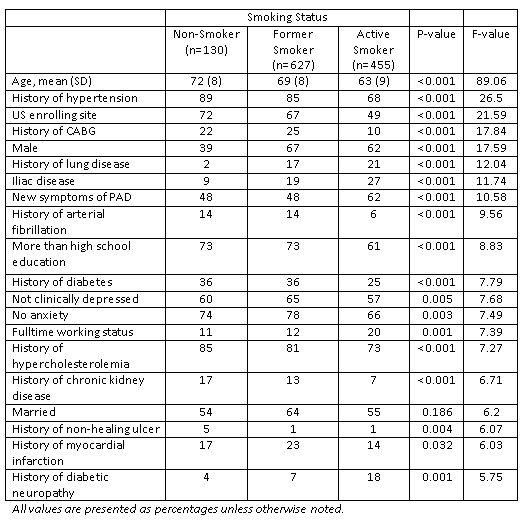
Methods: The Patient-centered Outcomes Related to Treatment Practices in Peripheral Arterial Disease: Investigating Trajectories (PORTRAIT) study is a multi-center global registry that enrolled 1,212 patients presenting with new symptoms or an exacerbation of symptoms of claudication at specialty clinics. Smoking status was verified through patient interviews before initial treatment. Demographic, socio-economic, and clinical information was obtained from patient interviews and medical record abstraction. The patient population was described by smoking status (non-smoking, former smoking, active smoking) and the F-values associated with the ANOVA tests were reported.
Results: Upon presentation, 38% of patients were actively smoking and 52% were former smokers. The top 20 characteristics associated with smoking status in claudication patients are listed in the Table. Several significant differences were observed. As compared with non-smoking patients, patients that smoked were younger, had an active working status, less cardiovascular risk factors, and presented with higher levels of depressive and anxiety symptoms.
Conclusions: Patients presenting with new or exacerbated symptoms of claudication that are active smokers have many different, prognostically important characteristics as compared with non-smokers. Comparative effectiveness research examining the association of smoking with outcomes needs to account for the vast differences in these patient populations.
Back to 2016 Karmody Posters
|







