|
Back to 2016 Annual Symposium Abstacts
3D Visualization of Radiation Scatter in Hybrid Operating Rooms: A Novel Tool to Examine Occupational Risks and Influence Radiation Safety
Yusuf Chauhan, BS1, Stephen Igo, BS2, Ponraj Chinnadurai, MBBS, MMST3, Thomas Loh, MD2, Matthew Bennett, MD2, Alan Lumsden, MD2.
1Texas A&M Health Science Center, College Station, TX, USA, 2Houston Methodist Debakey Heart & Vascular Center, Houston, TX, USA, 3Siemens Medical Solutions USA Inc., Hoffman Estates, IL, USA.
Objective
Advancements in catheter based device technology have increased the usage of real time X-ray image guidance in the hybrid operating room (OR). Despite the benefits and improved outcomes, these procedures pose occupational risks to surgical personnel. Long term radiation exposure has been correlated to the development of non-melanoma skin cancer, left sided brain tumors, pre-cataract lesions, and thyroid cancer. Our objective is to improve radiation safety measures by developing a tool for the 3D visualization and quantitation of radiation scatter in the hybrid OR.
Methods
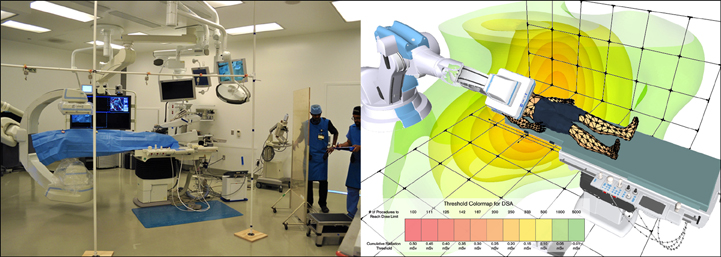
An array of 7 dosimeters (RaySafe i2®, Unfors Raysafe, Sweden) was constructed to collect real-time radiation data in a 16’x12’x6’ matrix within a hybrid OR equipped with a robotic C-arm based angiography system (Artis zeego®, Siemens AG, Germany). Radiation scatter data was collected from imaging studies performed on a human cadaver of BMI 20.2 using standard imaging modes (fluoroscopy (FL), digital subtraction angiography (DSA), cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)) across various C-arm angulations, dose levels, and extent of lead shielding. Radiation data was processed using 3D cubic spline interpolation across the matrix and visualized as mesh iso-surfaces based on occupational radiation limits.
Results
As demonstrated in the colormap for DSA (fig), a cumulative exposure 0.493 mSv for a single 10 second DSA limits the surgical personnel to performing 101 DSA scans (~17 minutes) prior to reaching the US N.R.C.’s 50 mSv annual limit. Cumulative radiation in AP was highest for DSA (0.227 mSv) followed by CBCT (0.086 mSv) and FL (0.028 mSv). Scatter was found to be highest for non-AP C-arm positions and consistently highest on the side of the emitter. Use of lead shielding demonstrated a decreased exposure in the shadow of the shield.
Conclusions
Our study is the first to visualize radiation scatter patterns in 3D space based on real-time data from experiments on a human cadaver in a hybrid OR. 3D visualization of backscatter radiation provides an intuitive and valuable means for understanding occupational radiation risks. By exposing these intangible patterns, we hope to create a paradigm shift in radiation safety education and create a demonstrable impact on occupational safety.
Back to 2016 Annual Symposium Abstacts
|







