One-stage Upper Arm Brachial-Basilic Arteriovenous Fistulas (BBAVF) Have Superior Patency Than Two-stage BBAVFs
Tze-Woei Tan1, Jeffrey Siracuse2, Karen Woo, MD, MS3, Donald Baril, MD3, Benjamin Brooke, MD, PhD4, Denis Rybin, PhD5, Alik Farber2.
1University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 2Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA, 3UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 4University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 5Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA.
Objective
An upper arm brachial-basilic arteriovenous fistula (BBAVF) is a reliable autogenous AVF that can be created using a one-stage or two-stage technique. Although both techniques are variably used, the optimal approach is uncertain. In this study, we compared the outcomes of one-stage and two-stage BBAVF procedures.
Methods
We examined 3498 BBAVF within the Vascular Quality Initiative Program (VQI) dataset (2010-2016) and compared one-stage and two-stage BBAVF procedures. Patients without any follow-up were excluded (n=999). Main outcomes included primary patency at 6-month and use for dialysis at 12-month. Other outcomes were wound infection, steal and swelling. Log-rank test was utilized to evaluate patency using Kaplan-Meier (KM) analysis and Cox multivariable regression models were used to examine the association between surgical technique and outcomes.
Results
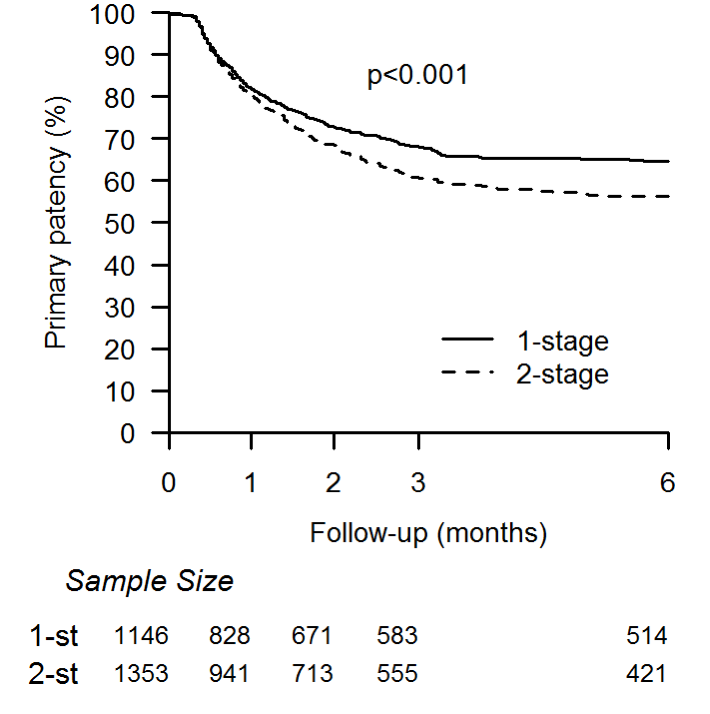
There were 1146 one-stage and 1353 two-stage BBAVFs in the study cohort. Over 70% of patients were on dialysis at the time of surgery, and 70% had a history of previous access. Patients who underwent one-stage BBAVF were more likely to be older, male, white, have no history of previous access, and have larger target vein than those treated with a two-stage procedure. Unadjusted KM analysis shows that 6-month primary patency rate was higher for one-stage BBAVF (69.2% vs. 63.5%, p<.001). On univariate analysis, although wound infection and steal were similar, arm swelling was greater for one-stage BBAVFs (2.3 % vs. 1.1%, p=.03). More one-stage BBAVF was used for dialysis at 12- month (43.1% vs. 25.5%, p<.001).
Multivariable analysis revealed that primary patency at 6-month was superior for one-stage BBAVF (Adjusted Hazard Ratio 1.2, 95% CI 1.0, 1.4, p=.02). One-stage BBVAFs had significantly more postoperative swelling (AHR 2.3, 95% CI 1.1, 4.6, p=.02) but were more likely to be used for dialysis at 12-month (AHR 1.7, 95% CI 1.3, 2.2, p<.001).
Conclusions
In the VQI cohort, one-stage BBAVFs were associated with superior primary patency at 6-month and were more likely to be used for dialysis compared to two-stage BBAVFs.
| Overall (N=2499) | One-stage (N=1146) | Two-stage (N=1353) | P-Value | |
| Characteristic | ||||
| Age | 61.3±14.6 | 61.9±14.6 | 60.8±14.6 | .03 |
| Male | 1735 (49.6%) | 869 (54.7%) | 866 (45.4%) | <.001 |
| White | 1648 (49.4%) | 919 (61.2%) | 729 (39.8%) | <.001 |
| DM | 2057 (58.8%) | 930 (58.6%) | 1127 (59.1%) | .764 |
| Dialysis | 2469 (70.6%) | 1142 (71.9%) | 1327 (69.5%) | .11 |
| Vein diameter | 3.8±1.2 | 4.1±1.2 | 3.5±1.1 | <.001 |
| Outcome | ||||
| Wound Infection | 17 (0.7%) | 10 (0.9%) | 7 (0.5%) | .30 |
| Steal | 49 (2.0%) | 25 (2.2%) | 24 (1.8%) | .51 |
| Swelling | 41 (1.7%) | 26 (2.3%) | 15 (1.1%) | .03 |
Back to 2018 Program




