Temporal Trends and Determinants of National Cost of AAA repair
Senthil Jayarajan, MD, Adrian Vlada, MD, John Maijub, MD, Abigail Barker, PhD, Patrick Geraghty, MD, Jeffrey Jim, MD, Luis Sanchez, MD.
Washington University in Saint Louis, Saint Louis, MO, USA.
Objectives: To investigate the cost trends for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair in the US and evaluate how different variables contribute to index hospitalization costs.
Methods: The 2001-2013 National Inpatient Sample database was queried for patients undergoing AAA repair. National estimates were calculated from weighted data and costs were inflated to 2013 dollar values. Slope analysis using linear regression was performed to assess temporal trends of index hospitalization costs. Linear regression of log costs was used to identify determinants of aortic repair costs.
Results: 128,154 aortic repairs, including 62,871 open repairs (OAR) and 65,283 endovascular repairs (EVAR), were analyzed. In 2013 the mean costs for the 2864 OAR and 6053 EVAR were $45034 and $32487 respectively. Inflation-adjusted costs of OAR increased from 2001 to 2013 by $4619 ($310/year, p<0.01), while EVAR costs decreased by $3104 (-$161/year, p=0.04). There was no change in costs of AAA rupture repair; the trends are due to changes in costs for intact repair. Whereas, large hospitals had increased costs for OAR ($402/year, p<0.01), there was no difference in EVAR cost trends by hospital size. OAR costs grew most at urban teaching hospitals ($507/year, p<0.01) while decreasing at urban nonteaching hospitals (-$264/year, p=0.03) and rural hospitals (-$458/year, p<0.01).
On univariate and multivariate analysis for hospitalization cost (Table), male gender, age <50 years and AAA rupture at presentation correlated with increased cost. The occurrence of any perioperative complications nearly doubled treatment costs in both OAR ($25,854 versus $51,734) and EVAR ($28,827 versus $44,995.).
Conclusions: As experience with EVAR has increased, the mean costs for the index hospitalization have declined. OAR costs have increased, especially at larger teaching hospitals. These changes in costs are observed only in intact AAA repair. This may reflect a shift toward EVAR for all but the most difficult elective cases. As scrutiny surrounding the cost and value of care intensifies, this data serves as a benchmark when developing and implementing strategies to lower the cost of AAA repair. 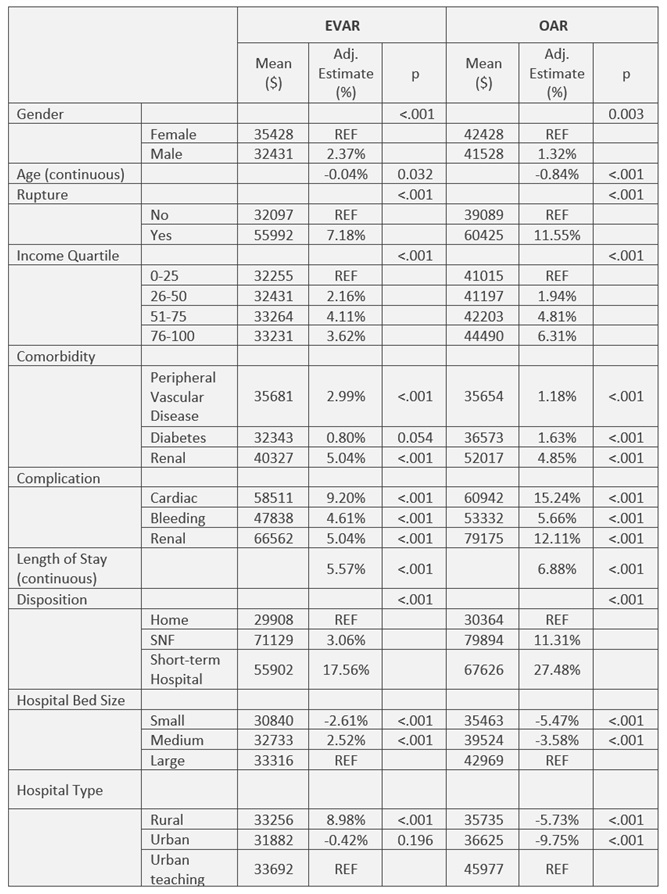
Back to 2018 Program




