Long Term Functional Outcomes after Revascularization of Acute Limb Ischemia
Ali Khalifeh, MD, Connor Oates, BS, Donald G. Harris, MD, George Makkar, MD, Nandakumar Menon, MD, Richa Kalsi, MD, Shahab Toursavadkohi, MD, Rajabrata Sarkar, MD, PhD, Robert Crawford, MD.
University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD, USA.
Long Term Functional Outcomes after Revascularization of Acute Limb Ischemia
Introduction:
Acute limb ischemia (ALI) is a common vascular surgical emergency. While initial technical options and short-term outcomes are well defined, long-term and patient centered outcomes are uncertain.
Methods:
Consecutive patients undergoing limb salvage for ALI at a vascular referral center were contacted for follow-up using a survey. General health status, limb function, and vascular health were assessed using the RAND SF-36, Lower Extremity Functional Scale, and Vascular Quality of Life instruments.
Results:
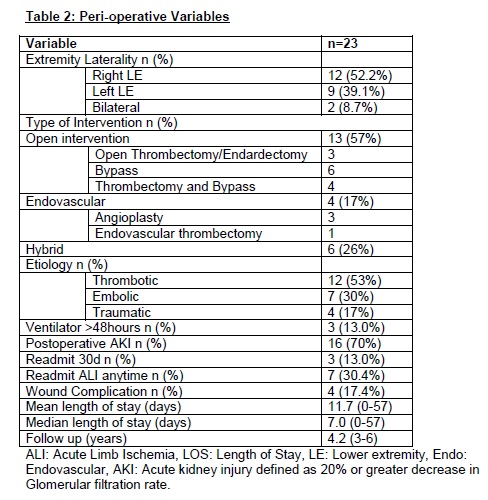
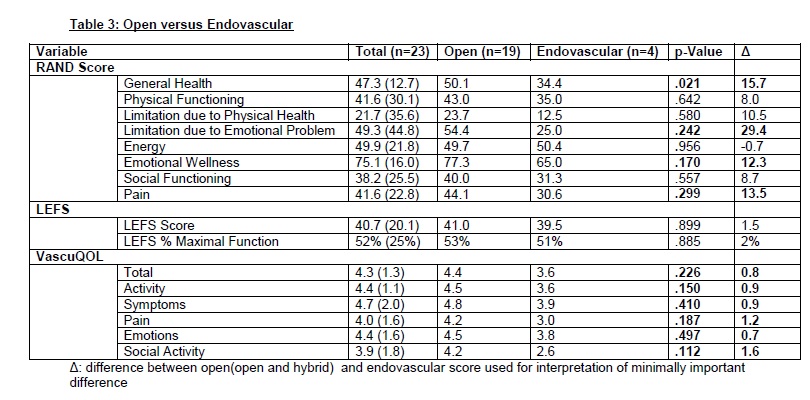
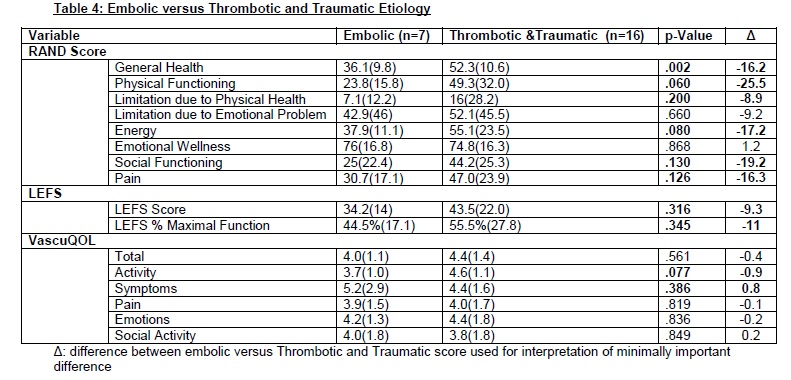
Of 190 patients eligible for inclusion, 23 (12%) responded to the survey. Median age was 66 years and 61% were male (Table-1). ALI etiologies included thrombosis (12, 53%), embolism (7,30%)and trauma (4, 17%). Revascularization was performed via open (13,57%), endovascular (4, 17%), and hybrid (6, 26%) procedures (Table-2). Median follow-up was 4 years (3-6). Indicating chronically impaired general and vascular health, and persistent limb dysfunction, all patients scored in the lower half of potential scoring range for each instrument. Treatment strategy was not associated with significant differences in long-term functional status, despite a trend for better score with open and hybrid approaches (Table-3). Patients that suffered from thrombotic or traumatic ALI had a trend for better long-term functional status when compared to embolic etiology(Table-4).
Conclusion:
Despite aggressive revascularization, ALI contributes to long-term impaired limb function and peripheral vascular health, and is a marker for compromised general health. Long-term follow up and aggressive postoperative medical and functional optimization may enhance limb and patient specific outcomes. Future studies of ALI management should include assessment of long-term and patient centered outcomes. 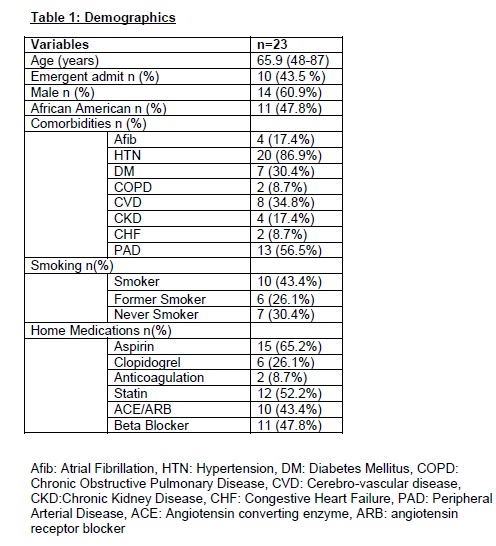
Back to 2018 ePosters




