Pore Size and Spacing of a Novel Shape Memory Polymer Wrap Induces Murine Neovascularization Subcutaneously in Order to Reduce Hemodialysis Access Site Failures
Timothy Boire, PhD1, Travis Vowels, MD2, Eric Peden, MD2
1Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA, 2Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
OBJECTIVES: Approximately 30-40% of arteriovenous fistulas (AVF) fail to mature, and 30% of those that do mature fail within the first year. Likewise, 80% of arteriovenous grafts (AVG) develop stenosis or thrombosis within the first year. Neointimal hyperplasia (NIH) at the arteriovenous or graft-vein anastomosis is the main source of failure. Several studies have demonstrated the promise of external stents to reduce NIH via promotion of neovascularization in the adventitia as well as through mechanical support. Limited clinical success of these approaches thus far may be due to inappropriate material selection (e.g. nondegradable, too stiff) and geometric design (e.g. pore size and spacing, diameter, length). Pore parameters affect the surface area-to-volume ratio and topology, and play a large role in the extent and type of inflammatory reactions observed (e.g.neovascularization). We investigate the influence of pore size and spacing on neovascularization for a novel external stent comprised of bioresorbable, thermo-responsive shape memory polymers (SMPs).
METHODS: Following an initial pilot, 21 mice were implanted with six scaffolds: four candidate SMP porous designs (A-D), nonporous SMP control (E), and GORETEX (F). Mice were sacrificed after 4 (N = 5), 14 (N = 8), and 28 (N = 8) days. Semi-quantitative scores were assigned in terms of the degree of neovascularization, inflammation, and fibrogenesis by a board-certified veterinary pathologist blinded to experimental conditions. Microvessel number, area, and density were quantified via a CD31 colorimetric microvessel detection algorithm.
RESULTS: There was a dramatic, statistically significant difference in the neovascularization score between all of the porous groups and nonporous SMP (p < 0.023) and microporous GORETEX (p < 0.007) controls at Day 28 (Figure). Follow up CD31 analysis suggested that the wider-spaced pore designs (Designs C and D) induced the most robust angiogenic response, with greater vessel numbers (p < 0.0016) and areas (p < 0.0038) than GORETEX at Day 28.
CONCLUSIONS: Macroporous SMP designs induced more neovascularization compared to non/microporous controls, and wider-spaced designs exhibited the highest total vessel number, area, and density. As this neovascularization is expected to in turn reduce NIH, this novel approach warrants further investigation in a large animal AVF/AVG model. 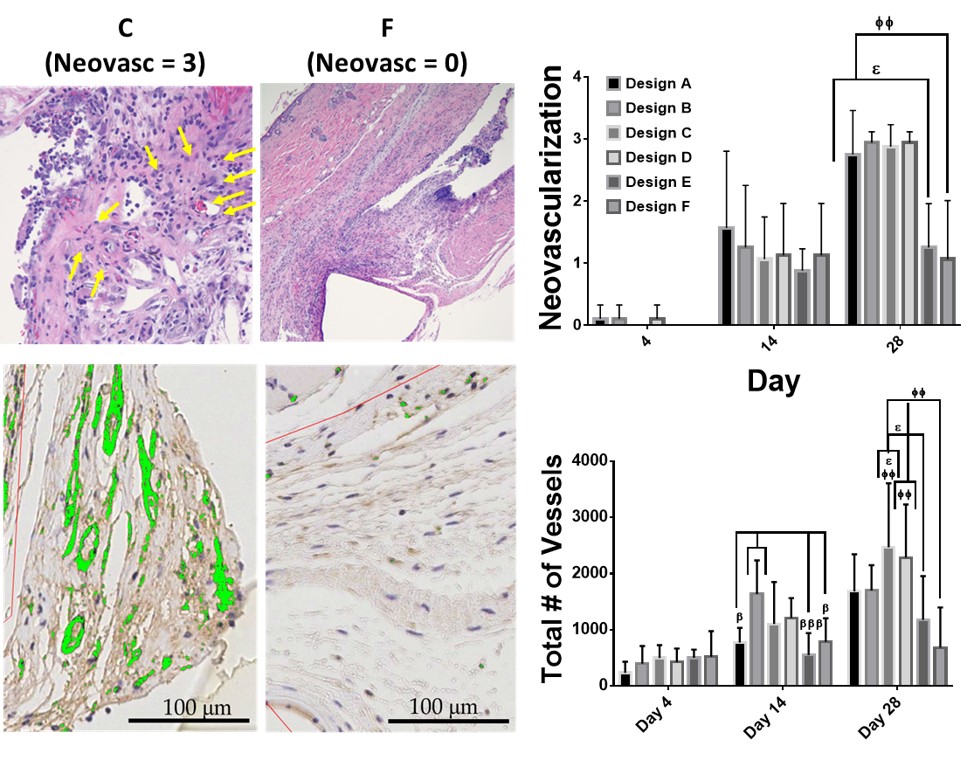
Back to 2019 ePosters
