Salvage of Carotid Artery Blowout in Patient with Heavily Irradiated Neck
Hunter M. Ray, MD1, Tam T. Huynh, MD2, Joshua D. Kuban, MD2, George T. Pisimisis, MD2.
1The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UT Health), McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX, USA, 2The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA.
DEMOGRAPHICS:
Therapeutic radiation is routinely used in head and neck cancer patients. In combination with radical neck dissection and carotid endarterectomy, may increase the risk for carotid artery aneurysmal degeneration and rupture.
HISTORY:
57-year-old male with history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the oral cavity treated with multiple neck dissections, flap reconstructions, and post-operative radiation (1997 and 2014) developed bilateral osteoradionecrosis, treated with subtotal mandibulectomy with osteocutanous free-flap reconstruction and concomitant carotid endarterectomy with patch for rapidly progressive critical stenosis.
PLAN:
Here, we present a case of endovascular repair of a large symptomatic pseudoaneurysm after disruption of carotid artery patch angioplasty in a significantly irradiated field.
DISCUSSION:
Three months after subtotal mandibulectomy, free-flap and carotid artery patch angioplasty he presented with acute neck pain and a contained carotid artery rupture, and also distal carotid kink and proximal stenosis from compression on CT (Fig 1A). There were no signs of localized or systemic infection. Endovascular repair was offered given the multiple redo neck operations, heavily irradiated field and the need for extensive length of extracranial carotid repair near the skull base. Via retrograde femoral access, the external carotid was coil-embolized and an 8x100mm Viabahn was used to exclude the degenerated length of carotid artery. The patient recovered without neurologic deficits and stent-graft was patent at 1-year follow up CT (Fig 1B). Endovascular salvage procedures may be safe and durable option for treatment in patients with carotid artery complications from adventitial degeneration related to prior radiation, radical neck dissection and carotid endarterectomy.
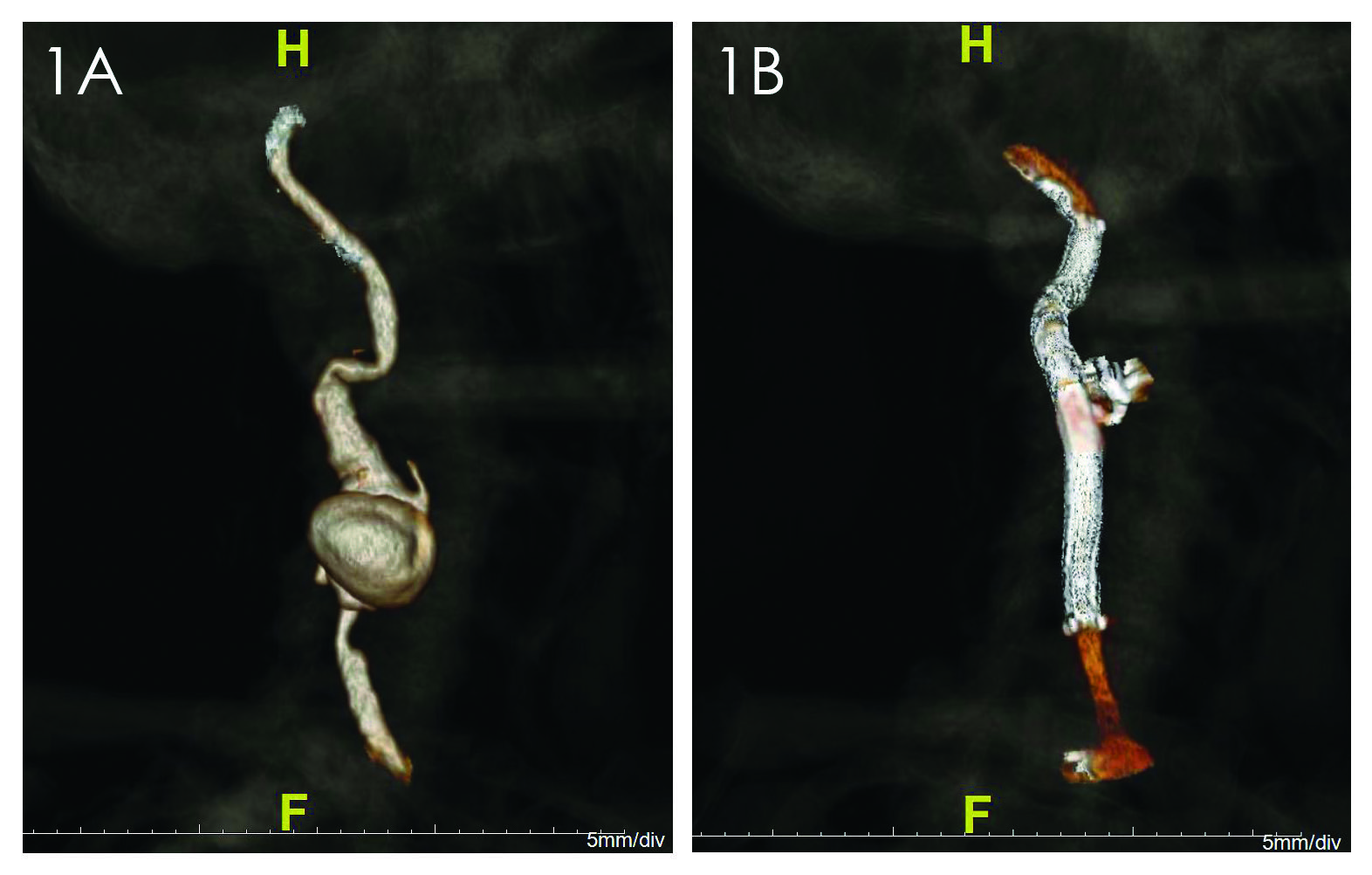
Figure 1: Preoperative CTA image demonstrating carotid artery pseudoaneurysm (1A); Postoperative CTA image at 1 year follow up demonstrating successful exclusion of carotid pseudoaneurysm (1B)
Back to 2019 ePosters
