Influence Of The Profunda Femoris Upon Primary Patency Following Inflow Procedures
Naveen Balasundaram, Jenna N. Whitrock, Drew J. Braet, Todd R. Vogel, Jonathon M. Bath.
University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, USA.
OBJECTIVES: The importance of the profunda for inflow procedure patency is well-recognized. We aim to quantify the characteristics of the profunda femoris and its relation to patency.
METHODS: We analyzed a prospective database of inflow procedures between 2009 and 2019 including aorto-bifemoral bypass (ABF), extra-anatomic bypass (EAB), femoral endarterectomy (FEA) and iliac stenting. Preoperative imaging characteristics of the profunda were reviewed as well as outcomes.
RESULTS: We performed 269 procedures in 202 patients. 162 were men (59.78%) and average age was 61 (SD 11.46). 123 patients (45.4%) presented with claudication, 69 (25.5%) with critical limb ischemia and 30 (11.1%) with acute limb ischemia. 50 patients (18.5%) underwent ABF, 43 (16.0%) underwent EAB, 58 (21.6%) underwent FEA and 158 (58.7%) underwent iliac stenting. 14 patients (5.2%) underwent FEA plus iliac stenting. 52 patients (19.2%) had an occluded superficial femoral artery. 24 patients (8.9%) had additional outflow procedures performed during the index operation; including lower extremity angioplasty in 10 patients (3.7%), lower extremity bypass in 10 (3.7%) and femoropopliteal thrombectomy in 5 (1.9%). Mean follow-up was 17.5 months with overall 2-year primary-patency (PP) of 79%. 2 year PP was 94.7% for FEA, 85.6% for ABF, 79.8% for iliac stents, 62.5% for EAB. Upon univariate analysis intervention thrombosis was associated with active smoking (20% vs 9.1% p=0.02), lower creatinine (Mean 0.84 + 0.15 vs 1.06 + 0.16, p=0.003), critical limb ischemia (25.45% vs 1.138%, p=0.03) and profunda with fewer than 5 branches >2mm in size (19.7% vs 5.7%, p=0.01). Multivariate analysis confirmed that a profunda with 5 or more branches >2mm in diameter was significantly associated with a lower risk of thrombosis (OR 3.45, 95% CI 1.16-10.3). The 2 year PP in these patients was 92.7% compared to 76% for profunda with fewer than 5 branches > 2mm.
CONCLUSIONS: Anatomic characteristics of the profunda are associated with patency of inflow procedures. Care should be taken to assess the main profunda and branch diameters on preoperative imaging. A concomitant infrainguinal procedure should be considered in cases of profunda with inadequate large branches, to ensure long-term patency of the inflow operation. 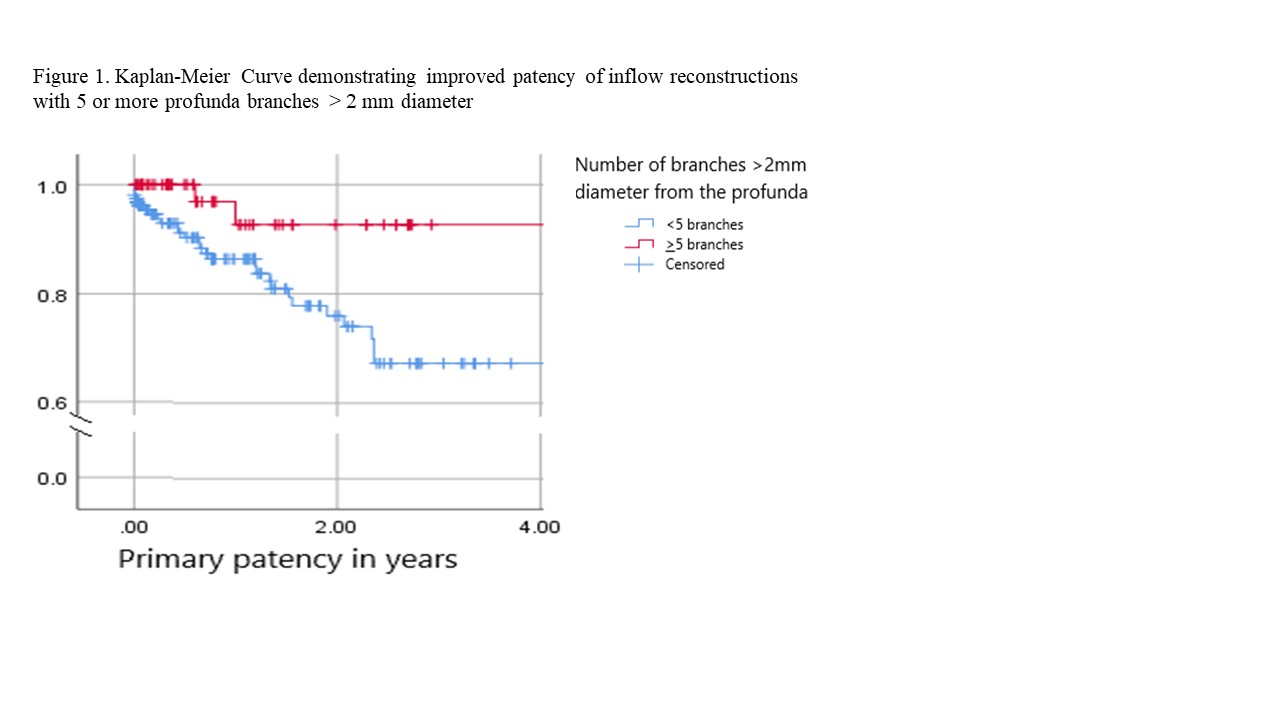
Back to 2021 Abstracts
