Five-year Survival Following Endovascular Repair Of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Is Improving
Rens R.B. Varkevisser, BS1, Nicholas J. Swerdlow, MD1, Livia E.V.M. de Guerre, MD1, Kirsten Dansey, MD1, Lars Stangenberg, MD2, Kristina A. Giles, MD3, Hence J.M. Verhagen, MD4, Marc L. Schermerhorn, MD1.
1Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA, 2Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI, USA, 3University of Florida Health, Gainesville, FL, USA, 4Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands.
OBJECTIVE: Increasing experience and improving technology have led to the expansion of endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). We investigated whether five-year survival following both EVAR and open repair for ruptured AAA changed over the last 15 years.
METHODS: We identified repairs for ruptured infrarenal AAA within the Vascular Quality Initiative registry (2004-2018). We compared five-year survival of both EVAR and open repair between the early (2004-2012) and late (2013-2018) cohort. In addition, we compared EVAR with open repair in the early and late cohort. We used propensity score modeling to create matching cohorts for each analysis. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to estimate survival proportions and univariate Cox proportional hazards analysis was used to compare differences in hazard of mortality in the matched cohorts.
RESULTS: We identified 4,638 ruptured AAA repairs. This included 409 EVARs in the early cohort and 2,250 in the late cohort, as well as 558 open repairs in the early cohort and 1,421 in the late cohort. Propensity matching resulted in 366 matched-pairs of late vs. early EVAR and 391 matched-pairs of late vs. early open repair. When comparing EVAR to open repair, propensity matching resulted in 277 matched-pairs of early EVAR vs. open, and 1,177 matched-pairs of late EVAR vs. open. In matched EVAR patients, five-year survival was higher in the late cohort (63% vs. 49%; hazard ratio [HR]: 0.77; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.61-0.97; P=.027; Figure A), while there was no difference between matched late vs. early for open repair patients (52% vs. 59%; HR: 1.04; 95%CI: 0.85-1.28; P=.69; Figure B). In the early cohort, there was no survival difference between EVAR and open repair (51% vs. 46%; HR: 0.88; 95%CI: 0.69-1.11; P=.28), while EVAR was associated with higher survival compared to open repair in the late cohort (63% vs. 54%; HR: 0.69; 95%CI: 0.60-0.79; P <.001).
CONCLUSIONS: Five-year survival following EVAR for ruptured AAA has improved over time, while survival following open repair remained constant. Consequently, the relative survival benefit of EVAR over open repair has increased over time, which should encourage further adoption of EVAR for ruptured AAA. 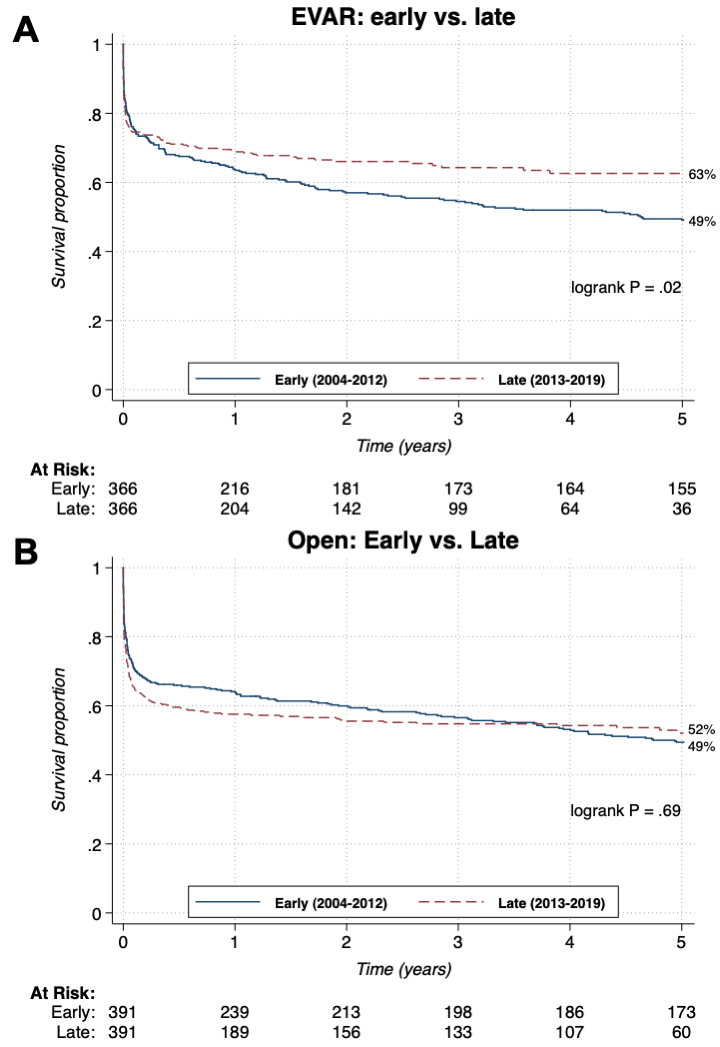
Back to 2021 Abstracts
