Bicycle Exercise Ankle-Brachial Index Recovery Time As A Novel Metric For Evaluating The Hemodynamic Significance Of External Iliac Endofibrosis In Competitive Cyclists
Kenneth Tran, MD1, Shernaz Dossabhoy, MD1, Sabina Sorondo, MD1, Jason T. Lee, MD2.
1Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2Stanford University, STANFORD, CA, USA.
Objective Subtle radiographic findings make the diagnosis of external iliac endofibrosis challenging. We have noted delayed recovery of ankle-brachial indices during exercise (exABI) on the affected limb in these patients. .This study sought to introduce and characterize a new metric, the bicycle exABI recovery time (BART), in a cohort of cyclists undergoing evaluation and treatment of external iliac endofibrosis. Methods A retrospective review was performed on consecutive patients undergoing treatment of endofibrosis at a single institution between 2011-2020. Patients with a pre-operative bicycle exABI test were analyzed. exABI tests were performed in a protocol until patients were symptomatic (e.g. onset of pain or cramping or loss of power). BART values were recorded, defined as the time in minutes required for a return of the ABI to 0.9 (Figure 1A). A post-operative survey was conducted to determine overall satisfaction. Results Of 36 patients treated for iliac endofibrosis, 24 patients were tested preoperatively with our exABI protocol and were included for analysis. 17 (70.8%) patients underwent patch angioplasty, four (16.7%) patients underwent bypass grafting , one (4.1%) patient underwent arterial resection with shortening, and one (4.1%) patient underwent stenting of the external iliac artery. All patients had a pre-operative exABI <.80 with radiographic evidence of external iliac arterial narrowing on CTA imaging with provocative maneuvers. BART values were ≥2 minutes in 24 (100%) patients, ≥6 minutes in 21 (87.5%) patients, and ≥10 minutes in 10 (41.6%) of patients (Figure 1B). Of patients with available post-operative BART recordings, 16 (76.2%) had at least a 50% decrease in BART post-operatively. Of patients who had available post-operative survey data, patients with >50% reduction in BART had higher levels of post-operative satisfaction (n=14, 100%) compared to those with <50% reduction (n=2, 50%) (p=.039). Conclusions Longer BART values assessed on pre-operative exercise vascular testing is a novel metric for measuring the degree of hemodynamic compromise in patients with iliac endofibrosis. Post-operative improvement in BART may also correlate with patient satisfaction. Given the rarity of this disease, we propose BART be measured in cyclists as clinical marker of disease severity and tracked postoperatively to document hemodynamic improvement. 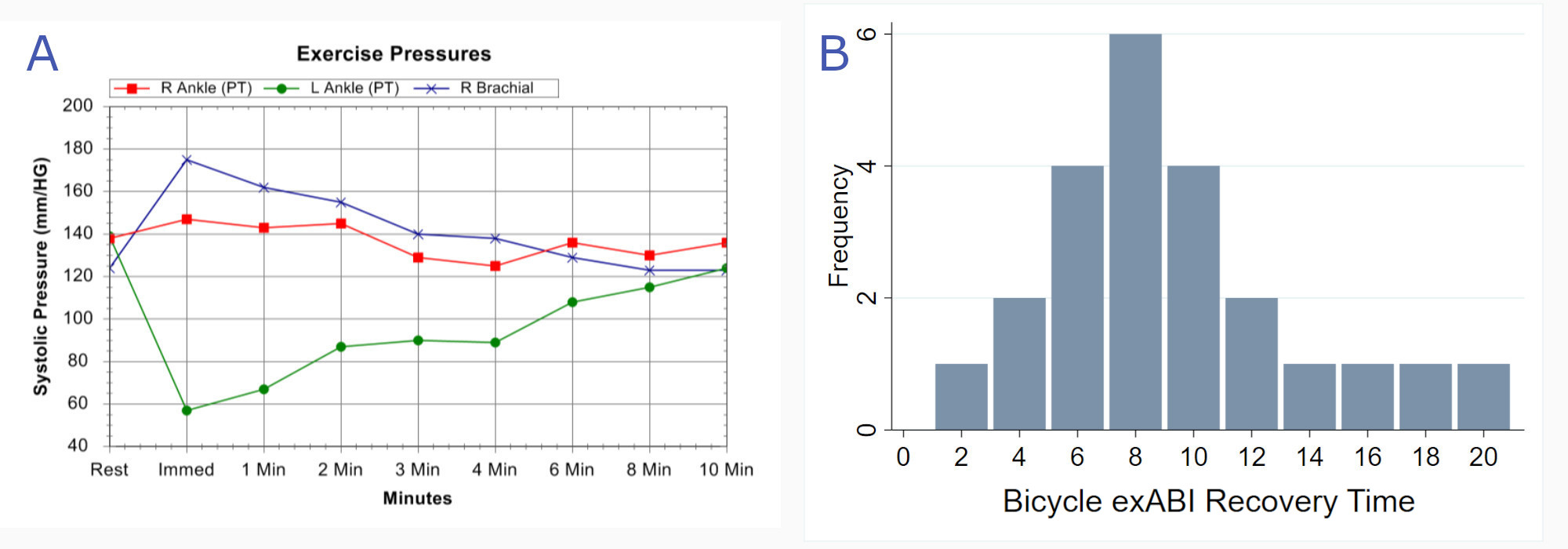
Back to 2021 Abstracts
