Percutaneous Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair With Monitored Anesthesia Care Decreases Operative Time But Not Pulmonary Complications
Joshua P. Kronenfeld, MD, Emily L. Ryon, MD, MPH, Alex Lall, MD, Naixin Kang, MD, Hilene DeAmorim, PA-C, Stefan Kenel-Pierre, MD, John Karwowski, MD, Arash Bornak, MD.
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine & Miami VAMC, Miami, FL, USA.
OBJECTIVES: Endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR) can be performed using different access types and anesthetic modalities, which can in turn impact patient outcomes. This study reports our experience and compares the results of percutaneous endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (PEVAR) performed under monitored anesthesia care (MAC), PEVAR under general anesthesia (GA), and EVAR performed with femoral cutdown (FC).
METHODS: A retrospective review of patients who underwent non-emergency EVAR between 2010-2019 was completed. Patients were excluded if they had a complex repair, including fenestrated, branched, or parallel endografting. Demographics, operative data, 30-day mortality/morbidity and postoperative outcome were analyzed. We compared the outcomes of the subgroups PEVAR under MAC, PEVAR under GA, and EVAR with FC.
RESULTS: 159 patients were identified with a median age of 69 (IQR: 58,70). 115 had PEVAR, with 45 (39.1%) MAC and 70 (60.9%) GA. PEVAR MAC compared to GA had decreased procedure time (106 vs. 134 minutes, p<0.001), time in the operating room (163 vs. 245 minutes, p=0.02), and estimated blood loss (EBL) (115 vs. 176mL p=0.01). There was no statistically significant difference in hospital length of stay (LOS) (1.9 vs. 2.7 days, p=0.13), and overall complications including pulmonary (2.2 vs. 2.9%, p=0.84), or urinary tract related complications (4 vs. 11%, p=0.401). 44 patients had EVAR with FC, including 14 PEVAR conversions. PEVAR conversion was associated with higher EBL (543 vs. 323 mL, p=0.03), procedure time (230 vs. 178 minutes, p=0.01), and operating room time (307 vs. 275 minutes, p=0.14) compared to planned EVAR with FC.
CONCLUSIONS: PEVAR under MAC compared to PEVAR under GA has shorter operative time, but has not significantly lower hospital length of stay, post-operative urinary tract or pulmonary complications. Patient selection, coordination between the patient, anesthetist and surgeon, as well as surgeonís expertise plays an important role in successful interventions under MAC. 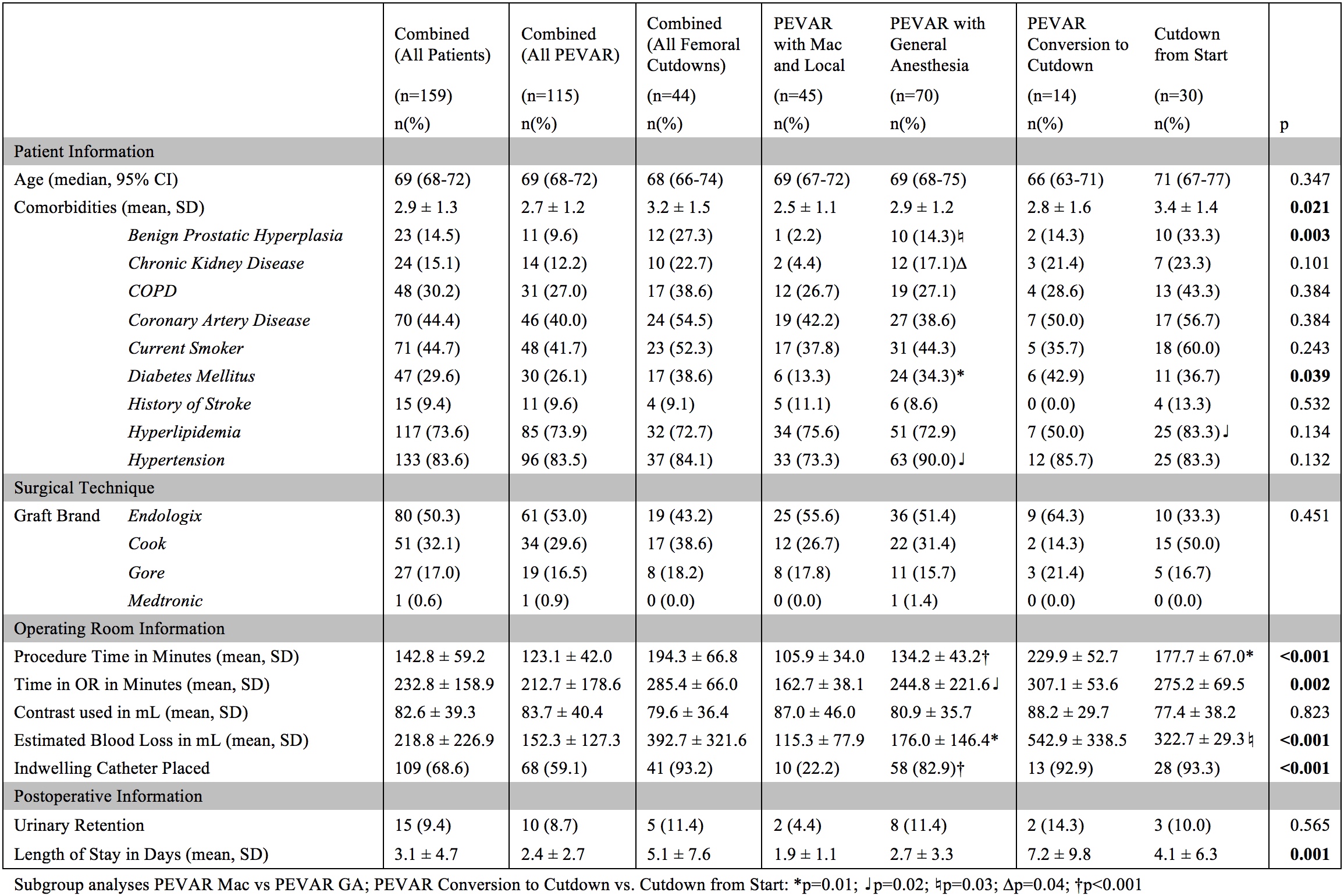
Back to 2021 ePosters
