Outcomes In Endothelioma - A Seer Based Study.
Qi Yan, Mark G. Davies.
UT Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, USA.
OBJECTIVES: Endothelioma is a rare vascular tumor. The management and outcome of endothelioma is not well described. The aim of this study is to report the patient demographic, tumor characteristic, and outcomes based on population data.
METHODS: Data on patients with endothelioma were obtained from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Statistical analysis was performed using Cox regression and with RStudio.
RESULTS: : 670 patients (46.9%, male; median age 51, IQR 37-66) with endothelioma were identified in SEER database between 1975-2006. Patient were mostly non-Hispanic Caucasian (68.5%), followed by Hispanic all races (12.2%), African American (9.9%), Asian or Pacific Islander (7.9%), American Indian/Alaska (0.6%), and unknown (0.9%). Median tumor size was 33 (IQR, 20.0-58.8) mm. Tumor grades were low to moderate on presentation (Grade I -7.9%; Grade II - 11.0%; Grade III 4.6%; Grade IV-3.7%, unknown 72.7%). A third (32.8%) of patients had localized disease, 18.6% regional disease, and 27.5% had metastasis, 21.2% were unstaged. Endothelioma most commonly involved soft tissue other than head and neck (37.8%), followed by soft tissue of the head and neck (28.8%), then bone (14.5%), breast (9.0%), visceral (0.9%), other (9.1%). Majority of the patients(81.2%) did not have a second primary malignancy aside from endothelioma. 36.4% of patients underwent surgery alone, 19.5% underwent surgery with radiation or chemotherapy, 5.8% underwent radiation only, 11.3% received chemotherapy only, and 36.4% had radiation and chemotherapy. The 5yr overall survival was 54.5% (95% CI 50.5-58.4%). Head and neck location (HR 0.79, P<.001), surgery (0.67, P<.001), surgery and radiation (0.60, P<.001), surgery and chemotherapy (0.78, P=.01), surgery, radiation and chemotherapy (0.70, P<.001) were associated with improved survival while visceral location (0.79, P<.001), larger tumor size (1.02, P<.001) were associated with worse survival. Radiation or chemotherapy were not associated with improvement in survival.
CONCLUSIONS: Endothelioma is a rare tumor with 5-yr survival of 54.5%. Chemotherapy and radiation are not associated with improved survival. Surgical resection alone or with chemotherapy or radiation offer significant benefit for survival and should be considered as the optimal paradigm . 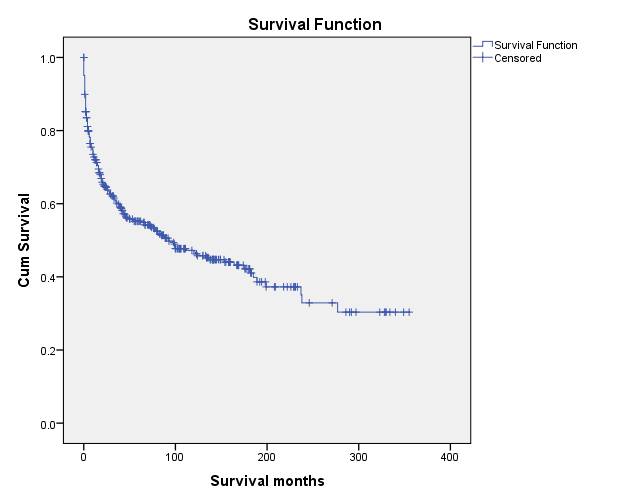
Back to 2021 ePosters
