Iliac Artery Pathology Presentation And Management In Vascular Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
Asmaa El-Ghazali, BS, Stephanie E. Wallace, MS, Kyle Wu, Jimmy Nguyen, BS, Peter Byers, MD, Sherene Shalhub, MD, MPH.
University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
Objectives: Iliac arteries pathology is encountered in patients with vascular Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (VEDS). We describe the presentation, management, and surgical outcomes among individuals with genetically confirmed VEDS. Methods: This is a cross sectional analysis of pathogenic variants in COL3A1 enrolled in the global natural history study, the VEDS Collaborative Research Study, from 7/2019-2021. Patients with common, external, and internal iliac artery (CIA, EIA, IIA) aneurysms/dissections were selected for descriptive analysis. Results: Among 321 individuals, 78 (24%) had iliac arteries pathology (50% male, 88.6% White). Mean age at VEDS diagnosis was 35.1+13.9 years and 39.2+11.7 years at iliac artery pathology diagnosis (no sex differences). Variant type was missense (61.5%), exon skip (15.4%), Null/haploinsufficiency (17.9%), and other (5.2%). History and exam findings included: 44.9% family history, 42.3% easy bruising, 24.4% hypertension, 7.7% smoking, 26.9% characteristic facial features, 25.6% joint hypermobility, 10.3% tendon rupture, and 3.7% club foot. Associated carotid, visceral, and aortic pathology was present in 38.5%, 44.9%, and 41% respectively. Location was CIA (n=49 (75.4%), 24 bilateral, 29 aneurysms, 19 dissections), EIA (n=32 (49.2%), 10 bilateral, 6 aneurysms, 20 dissections), IIA (n=4), and 2 unknown iliac location. CIA pathology presented with a bell-bottom configuration sparing the origin of the CIA (figure 1). CIA and EIA pathology was symptomatic in 12 and 14 cases respectively. The largest median CIA aneurysm size was 22 mm (range 16-74 mm). Surgery was performed in 17 (21.8%) cases: 11 open (3 aortobiiliac, 1 aortobifemoral, 3 iliac-iliac, 2 iliac-femoral, 1 femoral-femoral and 1 hematoma evacuation only) and 6 endovascular (1 endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR), 1 EVAR with branched iliac device, and 4 iliac artery stent grafts). None had a postoperative mortality. 10 patients (12.8%) died due to iliac artery rupture (n=2), aortic related (n=4), spontaneous coronary artery dissection (n=1), and 3 unknown etiology.
Conclusions: Iliac artery pathology frequently affects individuals with genetic VEDS, warranting surveillance. While the arterial tissues are known to be fragile, surgical outcomes are acceptable and lifesaving.
Figure 1 3D reconstruction of the aorta and iliac arteries in two patients show bell-bottom configuration sparing the origins of the common iliac arteries 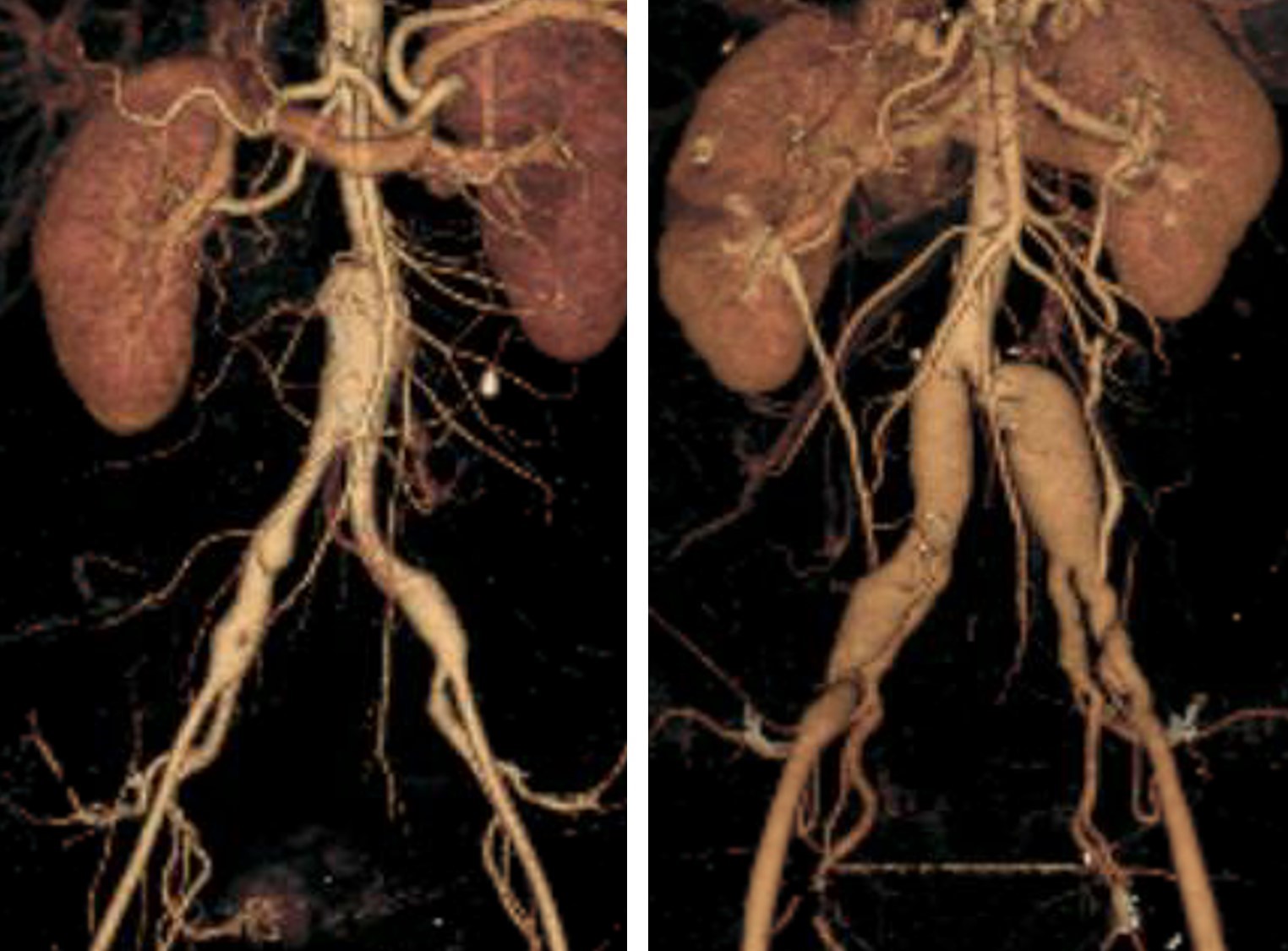
Back to 2022 Abstracts
