The Impact Of Practice Patterns On Outcomes And Costs In Acute Limb Ischemia
Ryan Gupta, MD, MBA, Michael Bronsert, Donald Jacobs, MD, Mark Nehler, MD, Jeniann Yi, MD.
University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, USA.
Objectives: We queried our statewide All Payer Claims Database (APCD) to identify acute limb ischemia (ALI) patients and determine regional practice patterns, impact of perioperative factors on ALI outcomes, and costs associated with the management of ALI.
Methods: A previously validated coding tool was used to identify ALI patients in APCD undergoing intervention 2012-2019. Demographic, procedure, cost, and morbidity details were compiled and multivariate analysis was conducted for primary outcomes of one-year readmission and reoperation.
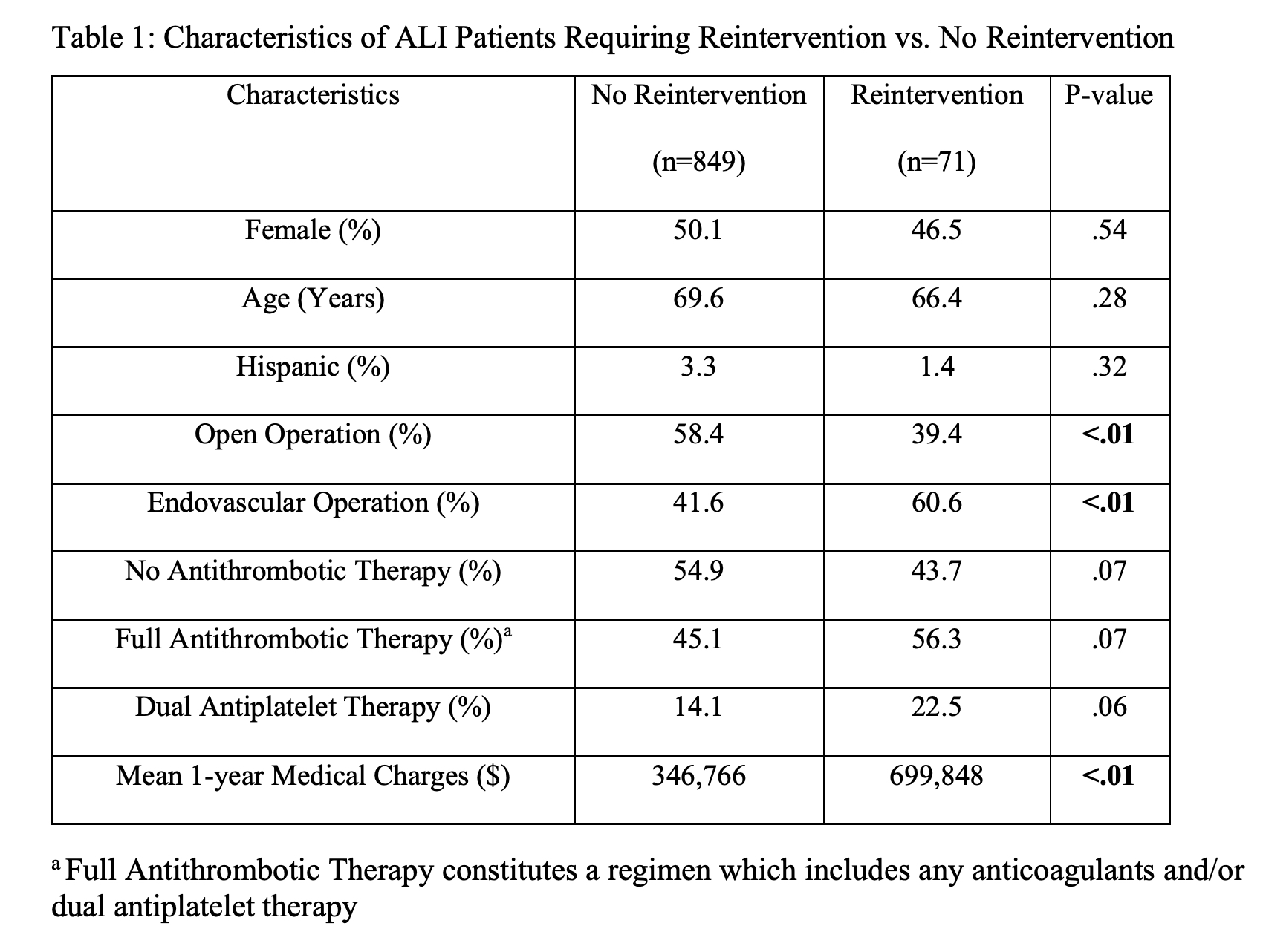
Results: 920 ALI patients were identified; 57.0% (n=524) underwent index open operation and 43.0% (n=396) underwent endovascular intervention. The overall readmission rate was 53.0% and reoperation rate was 7.7% (Table 1). Patients undergoing endovascular intervention were significantly more likely to require reintervention (10.8% vs. 5.3%, p<.01) but had similar rates of readmission (53.8% vs. 52.3%) to open surgical patients. Post-operatively, 35% of patients were placed on vitamin-K antagonist, 16% on antiplatelets, 12% on heparin, and 7% on direct-acting oral anticoagulants. In patients receiving full antithrombotic therapy - regimen including any anticoagulants and/or dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) - readmissions rates (58.6% vs. 48.1, p<0.01) and reoperation rates (9.4 vs 6.2%, p=.07) were higher than in patients without post-operative pharmacotherapy. Patients on DAPT had similar rates of readmission (58.8% vs. 51.9%, p=.14) and reoperation (11.7% vs. 7.0% p=.07) compared with those not on DAPT. One-year medical charges were significantly higher in ALI patients undergoing readmission ($558,632 vs. $165,955, p<.01) or reintervention ($699,848 vs. $346,766, p<.01). The most
common causes of reintervention were endovascular thrombectomy or other revascularization (40.1%), open thrombectomy (32.5%), and lysis catheter placement (21.2%).
Conclusions: Using a statewide claims database, we identified ALI cases and analyzed ALI practice patterns within the state over a 7-year period. The data underscores the morbid and costly nature of ALI care including a readmission rate of 53%, reintervention rate over 7%, and one-year mean medical charges as high as $700,000 in patients requiring reintervention. Antithrombotic ordering patterns vary widely in our state, and we found that full antithrombotic therapy was associated with higher rates of reoperation and readmission, suggesting a more conservative regimen could prevent morbidity following ALI intervention.
Back to 2022 Karmody Posters
