Optimal Medical Management In Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia After Intervention Improves Patient Outcomes
Matthew Chang, MD, Monica O'Brien-Irr, MS, RN, Brittany Montross, MD, Joanna Shaw, BS, Hasan Dosluoglu, MD, Linda Harris, MD, Maciej Dryjski, MD, Mariel Rivero, MD, Sikandar Khan, MBBS.
University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, USA.
Objectives: Optimal medical management of chronic limb threatening ischemia (CLTI) includes use of antiplatelets, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, statins and smoking cessation, and remains underutilized. Participation in programs like Vascular Quality Initiative (VQI) offers opportunities to increase compliance. The objective of this study was to evaluate medical management practice patterns and its effect on survival and limb salvage in CLTI patients. Methods: Patients undergoing endovascular peripheral vascular interventions (PVI) for CLTI between 2012-2016, with at least 24-month follow-up were identified from VQI. Patient details including smoking status, medication use, overall survival (OS), amputation-free survival (AFS) and limb salvage (LS) were analyzed in SPSS with linear-by-linear association, single sample t-test and logistic regression. Results: 12,370 PVI were completed in 11,466 patients. There was a significant increase in infrapopliteal interventions (29.8% → 39.0%; P < .001) and PVI performed for tissue loss (59.1% → 66.5%; P < .001). Across the span of the study, there was increased use of dual antiplatelets (DAPT) (41.1% → 48.0%; P < .001), ACE-inhibitors (46.2% → 51.3%; P < .001), and statins (70.4% → 77.5%; P < .001), and a significant decrease in smoking (36.2% à 30.7%; P = .036). Combined use of DAPT, ACE-inhibitors and statins during follow-up increased from 33.6% → 39.6%, representing an 18% increase. Significant improvement in OS and AFS was noted over the years, but not LS (24-month OS, 90.9% → 93.7%; P = .002: AFS, 81.2% → 83.1%; P = .046: LS, 89.6% → 89.0%; P = .83). Independent predictor of OS was combined therapy with P2Y12 inhibitors, statins and ACE-inhibitors: (HR 0.61; 0.39 - 0.96, P = .034 Independent predictor of LS was DAPT: (HR 0.83; 0.79 - 0.87, P < .007). Conclusions: Use of antiplatelets, ACE-inhibitors and statins improved and smoking rates decreased over the study period, and was associated with improved OS. Overall LS remained unchanged, however, a subset of patients on DAPT showed improved LS. While medical management has improved, it remains far from optimal. Optimizing medical management and encouraging smoking cessation represent important quality improvement areas in the care of CLTI patients that can impact outcomes. 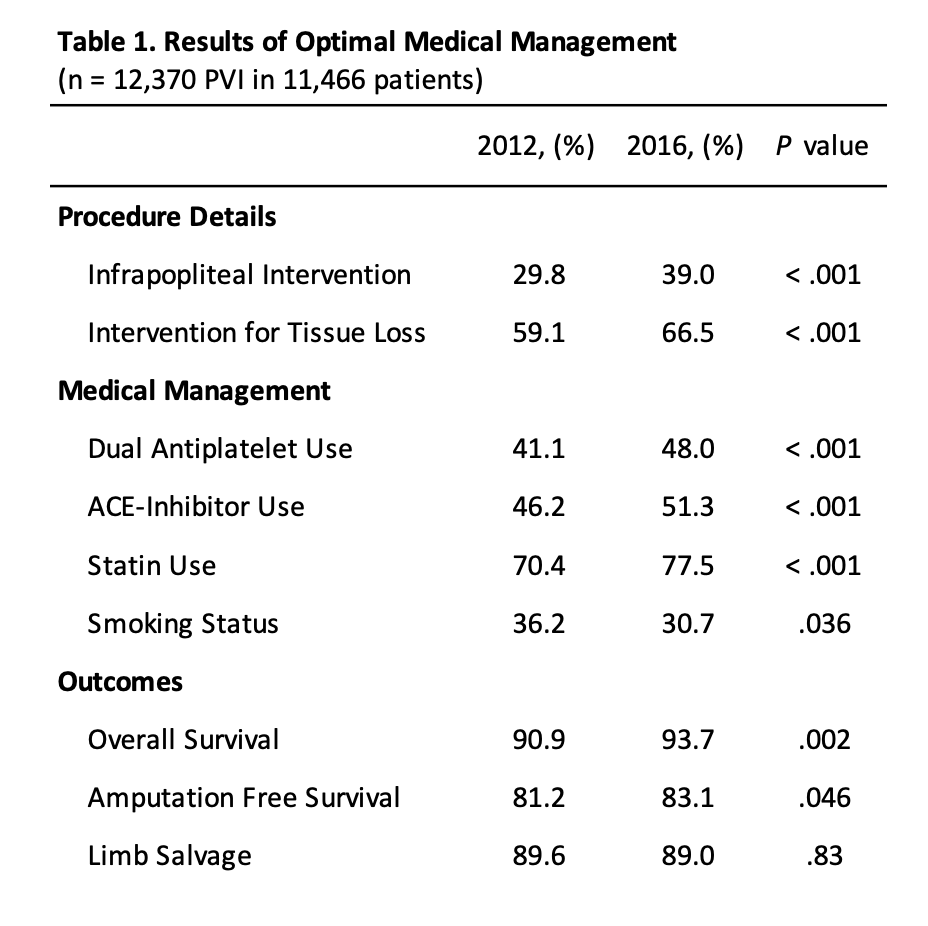
Back to 2022 Karmody Posters
