Increasing The Number Of Visceral Vessels Included In Endovascular Repair For Complex Aneurysmal Disease Does Not Adversely Impact Clinical Outcomes
Myra Ahmad, BA, Amit Pujari, MD, Blake Elizabeth Murphy, MD, Matthew P. Sweet, MD, Sherene Shalhub, MD MPH, Benjamin W. Starnes, MD, Sara L. Zettervall, MD MPH.
University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
Objectives: Endovascular approaches are increasingly utilized to treat complex aortic disease. However, the effect of number of target vessels treated has not been widely evaluated. This study describes outcomes of complex endovascular repair stratified by number of vessels treated.Methods: Patients who underwent endovascular repair with fenestrated endografts were identified in the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program by CPT code. They were stratified by the number of target vessels (TV) treated. Demographics, comorbidities, aneurysm extent, and 30-day outcomes were compared. Multivariate analysis was used to assess for predictors of adverse outcomes.Results: 418 patients underwent complex endovascular repair including 97 (23%) with 1 TV, 164 (39%) with 2 TV, 101 (24%) with 3 TV, and 56 (13%) with 4 or more TV. 287 complex endovascular repairs were performed for abdominal aneurysms, 64 for thoracoabdominal aneurysms, and 9 for dissections (p<0.001); 16 patients were treated for rupture (1 TV: 9%, 2 TV: 2%, 3 TV: 2%, 4 TV: 4%; p=0.01). When demographics and comorbidities were compared, age (72 years, 73 years, 74 years, 73 years; p<0.001) and current smoking (25%, 37%, 41%, 45%; p=0.043) differed between groups. Major complications (10%, 8.7%, 14%, 11%) and 30-day mortality were similar (4.5%, 6.8%, 7.1%, 1.9%), while operative time (233 minutes, 282 minutes, 288 minutes, 361 minutes; p<0.001) and hospital length of stay (3 days, 3 days, 4 days, 6 days; p<0.001) differed (Table 1). After multivariable analysis only prolonged operative time remained associated with 4 TV as compared to 1 TV (OR: 3.33, 95% CI: 1-10). While the number of target vessels treated was not associated with mortality, thoracoabdominal aneurysms (OR 9.4, 95% Cl: 1.4-65) and ruptured aneurysms (OR 12, 95% Cl: 3.3-47) were.Conclusions: There is wide variation in the number of target vessels treated with fenestrated repair. However, morbidity and mortality do not appear to be driven by the number of vessels treated. Instead, aneurysm extent and indication present as better predictors of adverse outcomes. The optimal approach to repair should be determined by the coverage required for complete repair and not restricted by the number of fenestrations needed. 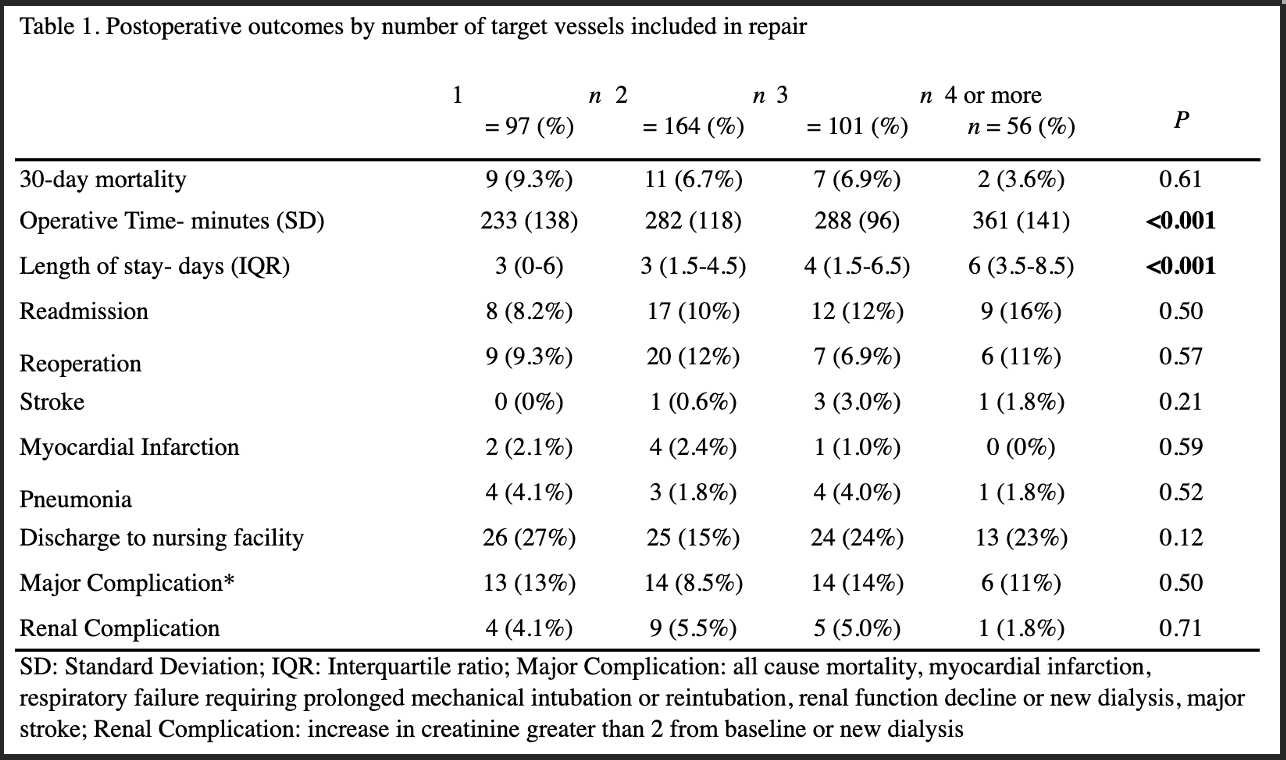
Back to 2022 Karmody Posters
