Renal Complications Following Juxtarenal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Impacts Late Survival And Repair Durability
Priya B. Patel, MD MPH, Christina L. Marcaccio, MD MPH, Thomas F. X. O'Donnell, MD, Ambar Mehta, MD, Karan Garg, MD, Sara L. Zettervall, MD, Jeffrey Siracuse, MD, Marc L. Schermerhorn, MD, Hiroo Takayama, MD PhD, Virendra I. Patel, MD MPH.
Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA.
OBJECTIVES: Renal complications following open and endovascular repair of juxtarenal aortic aneurysms are associated with increased postoperative mortality and morbidity. Our objective was to assess the impact of postoperative renal complications on late outcomes following juxtarenal aortic aneurysm repair.
METHODS: We identified all open and endovascular repairs of juxtarenal aortic aneurysms in the VQI from 2011-2017 with linkage to Medicare claims through 2018 for long-term outcomes. Juxtarenal aortic aneurysm repair was defined as placement of proximal clamp above at least one renal artery during open repair and treatment of at least one renal artery during endovascular repair. Postoperative renal complications included acute kidney injury(AKI), defined as ≥0.5mg/dL serum creatinine increase, or new renal replacement therapy(RRT). Kaplan Meier estimates and cox regression were used to identify the effect of AKI/RRT on late mortality, rupture, and reintervention. Three- and five-year outcomes are provided for open repair. Due to smaller sample size only three-year outcomes are provided for endovascular repair.
RESULTS: Of 1507 open repairs, 26% experienced postoperative AKI/RRT. Among elective repairs, AKI/RRT had higher rates of late mortality (3year: 8.7% vs 21%; 5year: 12% vs 25%;Log-P<.001), late rupture (3year: 5.7% vs 12%; 5year: 7.8% vs 14%;Log-P=.004), and late-reintervention (3-year: 6.3% vs 12%; 5year: 11% vs 20%;Log-P=.009).(Figure) AKI/RRT was also independently associated with higher risk of late mortality (aHR 3.5; 95%CI[2.3-5.3]) and trended towards an association with higher risk of late rupture (aHR 1.8[.98-3.4]) and late reinterventions (aHR 1.4[.80-2.7]).Of 933 endovascular repairs, 16% experienced postoperative AKI/RRT. Among elective repairs, AKI/RRT was independently associated with higher risk of 3-year mortality (12% vs 37%; aHR 2.2[1.6-30]), and late rupture (11% vs 18%; aHR 1.6[1.0-2.6]), but similar risk of late reintervention (18% vs 20%; aHR 1.6[1.0-2.6]). CONCLUSIONS: Postoperative renal complications were more frequent following open repair. However, late mortality, rupture, and reintervention occurred more frequently in patients with renal complications after endovascular repair. This calls into question the use of routine endovascular repair in patients with aortic aneurysm particularly those with underlying renal impairment. Furthermore, our study calls for optimization of preoperative renal status and the use of protective adjuncts and technique to prevent postoperative renal complications. 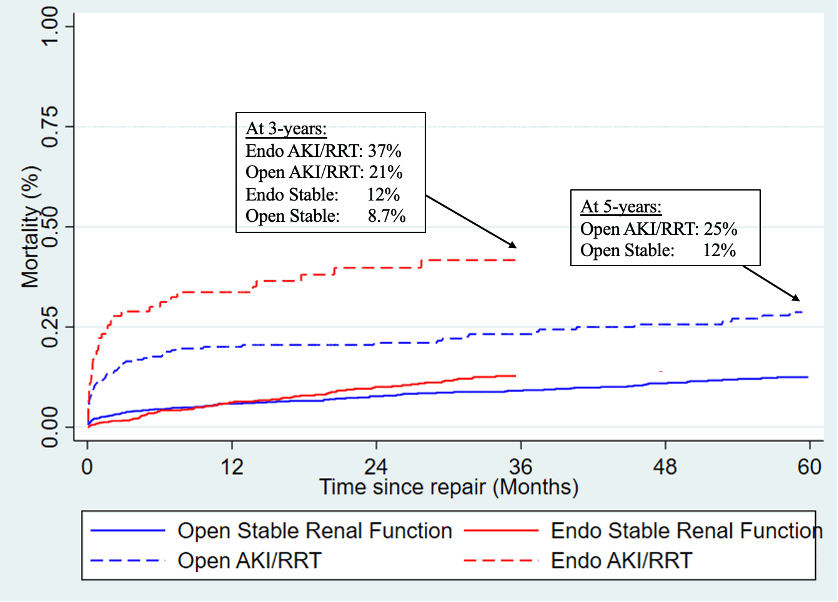
Back to 2022 Karmody Posters
