IVC Thrombosis And Pregnancy
Estela Abich, MD, Edgar Guzman, MD.
Orlando Health, Orlando, FL, USA.
Demographics
33-year-old G3P2 female with a 14-week gestation.
HistoryTwo weeks prior to presentation, our patient developed a right iliofemoral venous thrombosis with IVC involvement that was treated percutaneously at an outside hospital and started on low molecular weight heparin. She noted initial improvement, but redeveloped swelling and pain involving the right lower extremity, and new onset severe swelling and pain of the left lower extremity. Workup demonstrated an acute left iliofemoral DVT and recurrent right iliofemoral DVT. A diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia was also made and she was transitioned to argatroban.
PlanUnaddressed IVC thrombosis was suspected as the root cause of her right sided recurrence and new left sided thrombosis. We discussed IVC and bilateral iliofemoral thrombectomy and reconstruction, with the goal of intervention being relief of her present symptoms and reduction of post-thrombotic symptoms in the long term. Alternatively, reduction of risk to the fetus, avoidance of pulmonary embolism, and further thrombotic events would be favored by anticoagulation alone; the patient chose to pursue intervention.
DiscussionLow dose fluoroscopy, collimation, reduction of DSA runs and heavy reliance on intravascular ultrasound were used to minimize radiation exposure. The calculated fetal radiation dose was 62mGy, well below the 500mGy threshold for fetal harm at 14 weeks gestation. The calculated risk of childhood cancer was between 0.22-0.36%, equal to that of the general population. A penumbra Cath 12 device was utilized to remove acute and chronic burden. IVUS confirmed good clearance with persistence of pronounced atretic changes of the right iliofemoral system and IVC, as well as an arterial compression involving the left common iliac vein suggestive of May Thurner syndrome. Wallstents were used for the IVC and iliofemoral segments. The IVC bifurcation was reconstructed using Cook Gianturco Z stents. Postoperatively the patient experienced rapid improvement of symptoms and was discharged on apixaban without observed obstetric complications. Collaboration with the hematology and obstetric services were essential in assisting the patient understand her treatment options and risks. This case reinforces the importance of addressing IVC thrombosis and highlights techniques to utilize during pregnancy.
Figure 1.IVUS images pre and post intervention 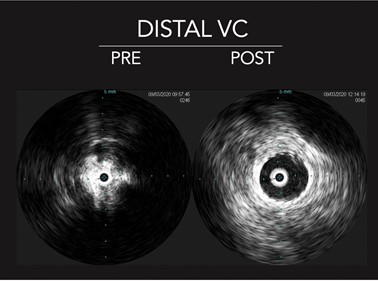
Back to 2022 Abstracts
